The
brain's
major
purpose
is to generate actions to interact with our environment. Sensory
inputs are the main sources of information used to guide these
actions. In my lab, we are interested in (1) how different
sensory inputs are combined to generate a unified representation
of the world that can then be (2) interpreted and transformed
into action plans which (3) control our different motor systems.
All three stages of this process are highly dynamic and
represent complex computational steps.
 Please find a list of equipment
available in my lab here
Please find a list of equipment
available in my lab here.
Some of the specific questions that we try to answer in the lab
are the following:
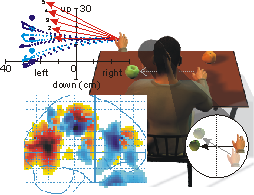
How and where does the brain perform the complete 3D
reference frame transformation of hand and target position for
reaching?
This research line
investigates how the brain performs the geometric
transformation between the incoming visual (and / or
proprioceptive) information of the hand and/or reach
target and the motor command sent to direct reaching arm
movements. I'm interested in how position and velocity
signals are used and combined in the brain in a
geometrically optimal fashion to produce accurate
behavior. Investigating this issue involves modeling of
the underlying geometry, a neural network approach to
address how this transformation could be performed by
distributed processing in the brain and functional brain
imaging to uncover where and when in the brain these
processes take place.
|
|
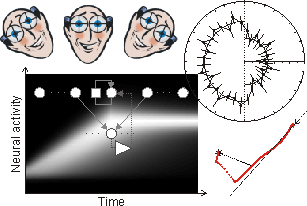
Where and how does the brain use
3D position and velocity signals for saccade and smooth
pursuit control?
Smooth pursuit and
saccadic eye movements interact a great deal. Saccades
can occur during smooth pursuit and in addition the head
can move during a pursuit movement as it can during
saccades. As a result we have 3 control systems
(saccade, pursuit and head) that have to be coordinated
in time in order to produce accurate and optimal
combined behaviour. The use of retinal and extraretinal
3D position and velocity signals in this control problem
are of special interest to me. How can we generate
geometrically accurate combined eye and head movements?
How is visual information transformed into motor
commands for the eyes and head. And how do higher-level
processes (e.g. attention) influence this eye-head
coordination for saccades and pursuit.
|
|
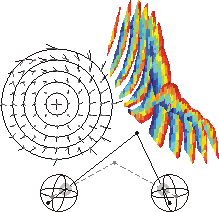
How are
different sensory sources used for perception and internal
representation of 3D space?
We
live
in
a
3D environment. However, most research investigating
perception and action in 3D space ignores the distance
dimension and considers space merely as a 2D surface.
Therefore, there are many unsolved problems and
questions concerning the use of 3D signals in perception
and the internal representation of 3D space for action.
For example, how can a 3D internal representation of
space be constructed from binocular vision in a
distributed processing scheme? Are the same 3D eye and
head position signals that are used for action also used
for perception? There are many open theoretical and
experimental questions to answer here.
|
|




